With how fast technology has advanced and how widely it’s spread, it should come as no surprise that computers now play a huge role in our everyday lives. From the smartphones we use to contact friends to the tablets we bring around to manage files, many of us are dependent (at varying lengths) on technology.
Therefore, it is important that we take charge of how and when our kids are introduced to the incredibly extensive – and sometimes complicated world of computers.
With that being said, here are some guidelines, suggestions, and recommendations CodaKid can offer regarding computer basics for kids.
Table of Contents
What are Computer Basics?
Computer basics refer to the bare-bones knowledge needed to properly operate – and interact with – a computer. This ranges from knowing the different parts of the computer to understanding how to use said parts to achieve a specific outcome. Computer basics are the foundation of computer literacy. Knowledge of the basics plus and correct application will lead to more extensive uses and processes later on.
In this article, we’re going to cover four basic computer skills for kids: input (how to use the mouse and keyboard), production (proper software and application usage), information gathering/research (how to use the internet safely and productively), and coding.

How Old Can Kids Start Using Computers?
Children as young as 3 years of age may start showing interest in the computer (or similar devices). Using tablets, laptops, and smartphones around them will pique their curiosity, and you may find them fiddling with these gadgets when in their immediate vicinity.
However, do not mistake this as a specific genuine interest in computers. Three- and four-year-old kids are pretty much in the “button-pressing” stage, and they will view computers as little more than fancy, shiny toys.
Four-year-olds may be able to discern letters and numbers on the keyboard. They may even be able to read what’s on the screen (simple terms like “Open,” “Close,” and “Okay,” especially). But as far as comprehension and deeper understanding of how to actually use a computer goes, they definitely won’t go further than surface level.
If a three- or four-year-old kid wants to use the computer, we strongly recommend limiting them to 5-10 minutes a day. And this goes without saying, but their “computer use” should translate to you taking complete control of the keyboard and mouse while they sit on your lap and observe. Click on whatever they may point at on the screen (if deemed appropriate) and maybe allow them to interact with it by way of typing.
Other than that, we feel that kids younger than 4 years of age shouldn’t use a computer by themselves for both practical, mental, and safety reasons.
So, how old can kids start using the computer? Our recommended ages would be between 5 and 7 years.
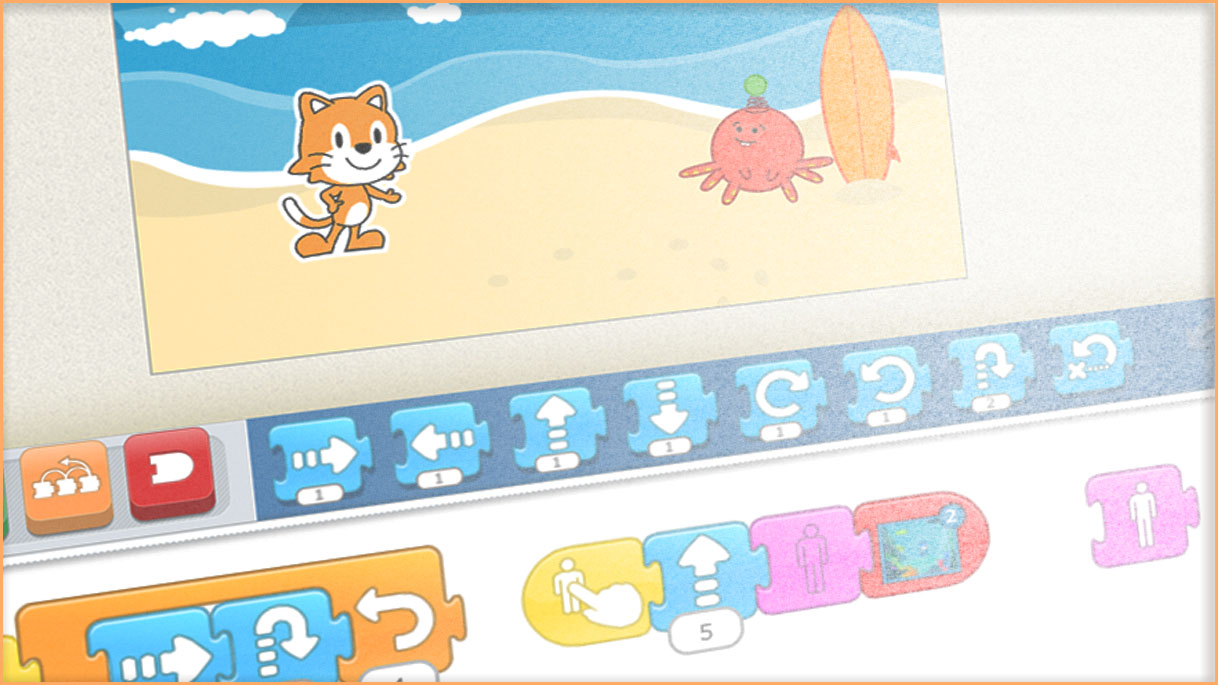
5-year-olds should have enough fine-motor skills and situational comprehension to properly use a computer with minimal adult supervision. In fact, a simplified version of the popular kids’ coding language, Scratch – known as ScratchJr – is specifically designed for ages 5 to 7. And, yes, there are definitely 5-year-olds out there capable of programming their own interactive stories and games!
Recommended Reading:
Here are some suggestions we have regarding 5-year-olds and computer usage:
- Stay with them as they use the computer, but let them have full control over the mouse and keyboard (unless they ask specifically for help)
- Screen the games they want to play and the websites they visit regularly. At this age, they most likely won’t be able to explore the internet as widely and as rapidly as older children can, but it’s always best to err on the side of caution
- That being said, introduce them immediately to basic internet and technology safety measures
- Limit their computer time! One to two hours a day is plenty. Only adjust the schedule if they have trouble completing a school project or activity within the allotted time

Should I Monitor my Child’s Internet Activity?
Although we 100% advocate encouraging independence and we also believe that kids are entitled to privacy, yes; we strongly recommend you routinely monitor your child’s internet activity. Especially for very young children.
As we mentioned earlier, kids aged 7 and below should always have an adult present to watch everything they’re doing on the computer (and to help them, should they need it). At the age of 8 or 9, children are old enough to understand the concepts of action, consequence, and causal effect. That is to say, they’ll know that breaking internet rules or experimenting with computer/internet settings could have unpleasant repercussions.
We think it’s safe to leave children aged 8 and up alone on the computer for extended periods (maybe no more than 30 to 45 minutes). But we still recommend placing a curfew or computer schedule—even for teenagers!
In the case of teens, tweens, and pre-teens, it may be difficult to monitor every online interaction they make. At their age, privacy is a big deal, so requesting full access to their social media accounts (so you can filter everything they post) may not be ideal.
But you can always opt for a compromise! Checking their browsing history on the regular isn’t as invasive and will give you a pretty solid idea of the websites/platforms they frequent.
Computer Basics for Kids: What They Should Know
Basic Keyboard and Mouse Skills
Pretty much the only way we can interact with a computer (barring the touch-screen ones) is by using either the keyboard or the mouse. So it’s important that kids learn keyboard and mouse skills as early as possible.
How to move the mouse, to control the cursor, the difference between a left-click and right-click, proper typing position (hand placement, etc.), different key groups (number keys, letter keys, special keys), and how to use keyboard shortcuts are just some examples of computer basics for kids.
Here are some elements you should highlight:
- What “special keys” like Enter, Shift, CTRL/CMD, and the space bar do
- How to use arrow keys to move around the screen
- Touch-typing
- Simple keyboard shortcuts like CTRL/CMD + V and CTRL/CMD + C
- “Hovering” over something versus “clicking” on it
- The difference between “left-click” and “right-click”
- Controlling the cursor by controlling the mouse (hand-eye coordination + fine-motor skills)

Basic Software and Application Skills
Once your child knows how to interact with the computer via input, it would be best to introduce the basic software, programs, and applications they’ll most likely encounter frequently. This includes programs for schoolwork (like Google Docs, Google Chrome, and Microsoft Word) and programs for leisure (such as YouTube, Facebook, and popular gaming platforms like Roblox).
Recommended Reading:
Older children will most likely be introduced to additional software at school in compliance with their lesson plans.
Here are some computer programs we feel kids should be familiar with early on:
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Excel
- Internet Browsers (Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.)
- Google Apps (especially Google Docs and Google Drive)
- Simple photo editing/drawing tools (like MS Paint)
- File Storage Programs (like Windows File Explorer)
These computer programs can teach your kids necessary computer skills like:
- How to drag + drop files
- How to rename folders
- How to share files
- How to create and save new word documents
- How to print word documents
- How to access the internet
And on the subject of the internet…
Basic Internet Introduction: Safe and Productive Use

Like it or not, the internet is now a crucial part of our daily lives. Computer literacy involves more than just knowing how to work with computers; it involves knowing how to access the internet to find – and verify – information.
Recommended Reading:
And given how easy it is to fake news and publicize unverified controversies today for the sake of entertainment, it’s crucial that students learn how to use the internet safely and productively. This includes familiarizing them with verified websites for information and apps that are safe to use.
For older kids, say aged 8 and up, showing them the importance of account security and safe search mode is paramount.
If you feel out of your depth, don’t worry; there are plenty of internet safety lessons for kids available. You can even ask the school for take-home pamphlets and resources for more info!
Part of safe and productive internet use includes:
- For older kids, knowing how to discern reputable/trustworthy news websites from unofficial/scrupulous ones
- For younger children, knowing the limits or rules to use apps appropriately
- For older kids, responsible media sharing (i.e., what they post to their social media profiles, what links/websites they circulate amongst their friends, etc.)
- How to evaluate information (the information itself plus its source)
- The importance of keeping personal information private
- For older kids, how to cite online sources properly
As parents, the best way to keep your kids safe online is to educate them. Communication and trust are key to your child having a healthy and responsible relationship with computers and digital media.
Coding Basics for Kids

Although some may believe that coding is too complex to even be taught to kids, there is a reason schools include programming basics as part of general computer literacy. Knowing how to code gives your child certain skills that they can use outside of programming. Knowledge of things like HTML tags, loops, and conditionals may seem a little more career-specific, but it’s definitely an advantage to have such know-how on hand.
Coding for kids is a little more extensive and a little less generalized than the other topics. But for the most part, teaching coding basics to kids would include:
- Introducing them to what they can do with programming
- Familiarizing them with different programming languages (especially the ones best-suited for kids)
- Familiarizing them with basic programming terms (like run, Java, C++, Scratch, ScratchJr, Loops, Statements, etc.)
- Providing practical applications of coding (games like Minecraft and platforms like Roblox)
Recommended Reading:

Tips for Teaching Kids Computer Basics
Once you introduce your child to the world of computers, there’s no going back. Regardless of how you may feel about it, technology is going to play a part in their life as they grow up. From mobile phone apps to social media platforms to online games, your child is going to interact with some form of computer or digital media.
The best thing you can do for them is to encourage responsible computer literacy. Teaching them the basics as early as possible (and as early as you deem appropriate) will prove to be beneficial to them in the long run.
Before we end this, here are a few professional tips we can offer when it comes to teaching computer basics for kids:
Encourage Communication.
It’s best if both student and teacher are as vocal as possible. Reassure children that it’s okay to ask questions. Reiterate guidelines and teaching points as often as possible. If possible, try to have open, honest discussions before or after your child uses the computer
Don’t Breach Their Privacy
We mentioned this earlier, but we feel it’s worth repeating.
For pre-teens, tweens, and teens, respect their privacy. Let them have their own social media accounts and emails. Do not snoop around in their conversations. Do not try to filter what they post or share.
As long as they’re still practicing safe and productive internet usage, there is no reason good enough to breach their privacy
Be Patient
In the case of younger children, things like computer interaction, input, and programming may have some pretty high-priced requirements (i.e., good hand-eye coordination, fine-motor skills, high-level comprehension, great memory, etc.).
If your child has trouble understanding and applying certain concepts, yelling or voicing your frustration isn’t going to help them. As with teaching kids anything, it’s best to be kind and patient.
Conclusion
Overall, you don’t need to formally teach your child computer basics. We’re willing to bet that their school will have a lesson plan or quick course on computer literacy to cover that. As their parent, your job is to supervise, elaborate, and clarify as needed.
Table of Contents
- What are Computer Basics?
- How Old Can Kids Start Using Computers?
- Should I Monitor my Child’s Internet Activity?
- Computer Basics for Kids: What They Should Know:
- Basic Keyboard and Mouse Skills
- Basic Software and Application Skills
- Basic Internet Introduction: Safe and Productive Use
- Coding Basics for Kids
- Tips for Teaching Kids Computer Basics
- Conclusion
Besides this, children easily soak up information just by watching and doing. So don’t be surprised if your child is much more competent at computers than you expected them to be!
Is your child ready to learn the basics of coding while playing fun games like Minecraft and Roblox? Enroll them in CodaKid’s free trial, today!